The Aichi Branch of Wild Bird Society of Japan
Egret Colonies in Kanie/Yatomi highway interchanges
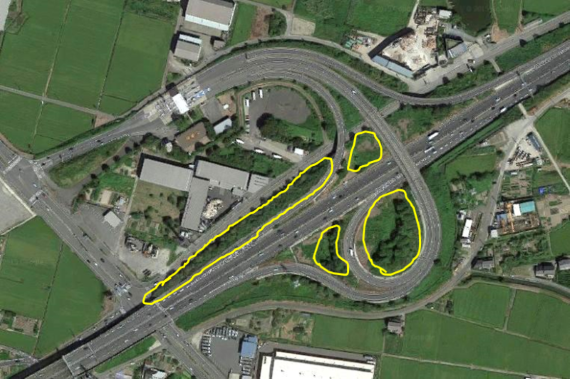
Kanie and Yatomi interchanges of the Higashimeihan Expressway are located from the west Nagoya city in Aichi prefecture to the Tsu city in Mie-prefecture. In every breeding season, six species of Egrets and Herons form breeding colonies in the loops of both interchanges. In 2015, the total number of herons and egrets in the interchanges was 7900, which may be one of the greatest numbers in egret colonies in Japan.
The species forming the colonies include Grey Heron (Ardea cinerea jouyi), Great White Egret (Ardea alba modesta), Intermediate Egret (Egretta intermedia intermedia), Little Egret (Egretta intermedia intermedia), Cattle Egret (Bubulcus ibis coromandus), and Black-crowned Night Heron (Nycticorax nycticorax). In both interchanges, the Intermediate Egret accounts for 43%-50% of the total population.
Suspected reasons why the Egrets/Herons have chosen the forest of Kanie and Yatomi interchanges are as follows:
1. A vast rice fields covered by a network of small streams suitable for feeding extends over the surrounding area of both interchanges.
2. No forest is available for their breeding around the both interchanges, however, only inside of the Kanie and Yatomi interchanges are forests suitable for breeding.
3. Central Nippon Expressway Company Limited (NEXCO-Central), the operation and management company for the Higashimeihan Expressway, have maintained and protected the forests of the interchanges as the nesting habitats for the Egrets/Herons.
A part of Kanie interchage colony
(Click to open the video of Kanie interchange colony)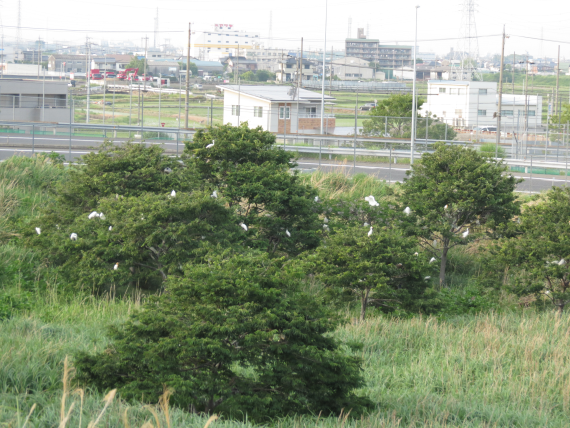 

A part of Yatomi interchange colony

Photograph of Kanie interchange colony from google map. The breeding areas are circled in yellow.
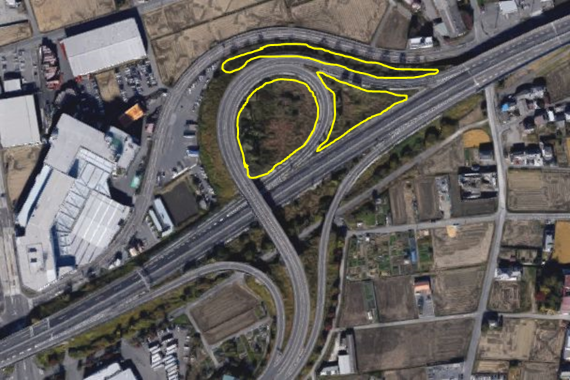
Photograph of Yatomi interchange colony from google map. The breeding areas are circled in yellow.